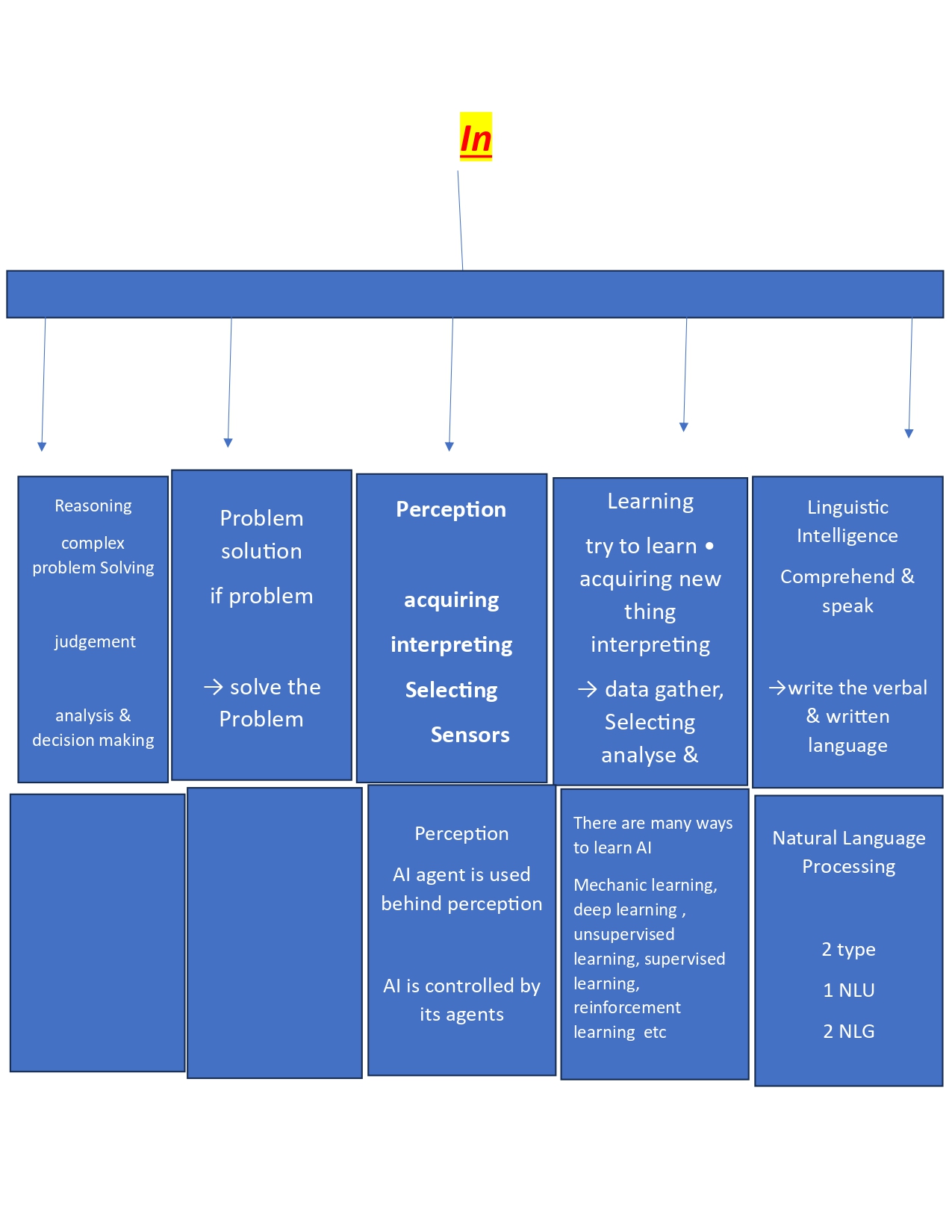
what is intelligence composed of
what is intelligence composed of
NOTE =
AI works together with all of them but it is the AI agent who gives you the results with their help.
That means you should know about AI Creative
Then you will know how to work after making
hindi =
ai ai इन सभी से मिलकर बना होता है परंतु आपको आई एजेंट ही आपको रिजल्ट उनकी सहायता से कार्य उपयोग किया जाता है
यानी कि आपको AI एजेंटों के बारे में जानकारी होनी चाहिए
तब आपको बनने के बाद कैसे कार्य करता है यह पता चलता आएगा
what is artificial intelligence composed of Reasoning =
is ka woek
- complex problem Solving
- judgement
- analysis & decision making
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a crucial role in various aspects of reasoning, complex problem-solving, judgment, analysis, and decision-making. Here’s how AI contributes to each of these areas:
- Reasoning: AI systems employ various reasoning techniques to process information and draw conclusions. These techniques include:
- Symbolic Reasoning: AI systems use logic and symbolic representations to manipulate and reason with information.
- Probabilistic Reasoning: AI employs probability theory to handle uncertainty and make informed decisions in uncertain environments.
- Fuzzy Logic: AI can deal with vague and imprecise information using fuzzy logic, enabling more nuanced reasoning.
- Complex Problem Solving: AI excels at solving complex problems through the following methods:
- Search Algorithms: AI algorithms, such as A* search or genetic algorithms, are used to find solutions in large solution spaces.
- Machine Learning: AI models, like neural networks and decision trees, can learn from data and make predictions, solving problems like image recognition, natural language understanding, and more.
- Optimization Techniques: AI is used to optimize resource allocation, scheduling, and other complex tasks.
- Judgment: AI systems can provide valuable judgment in different domains:
- Expert Systems: AI expert systems incorporate domain-specific knowledge to offer judgments and recommendations. For example, a medical expert system can provide diagnostic judgments.
- Sentiment Analysis: AI can analyze text and social media data to determine public sentiment on various topics.
- Analysis & Decision Making: AI aids in data analysis and informed decision-making through the following means:
- Data Analytics: AI processes vast amounts of data to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that human analysts might miss.
- Predictive Analytics: AI models can forecast future outcomes based on historical data, enabling proactive decision-making.
- Reinforcement Learning: In dynamic environments, AI can make sequential decisions by learning from feedback and experience.
what is intelligence composed of Problem solution
- Problem Identification: First, AI systems need to recognize and understand the problem. This can be achieved through various means, such as data analysis, sensor input, or user input.
- Data Collection and Analysis: AI collects relevant data and information related to the problem. This data can come from various sources, including sensors, databases, or the internet. AI then analyzes this data to gain insights and a better understanding of the problem’s context and scope.
- Pattern Recognition: AI algorithms are often used to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies within the data. These patterns can be critical in diagnosing the problem and formulating potential solutions.
- Hypothesis Generation: AI may generate hypotheses or potential solutions based on the data analysis. This can involve exploring different scenarios or considering historical data to find potential solutions.
- Simulation and Testing: In some cases, AI can simulate the problem and proposed solutions to evaluate their effectiveness. This allows for virtual testing and refinement before implementing a solution in the real world.
- Decision-Making: AI can employ decision-making algorithms to evaluate the generated hypotheses and select the most promising solution based on predefined criteria or objectives.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Once a solution is selected, AI can assist in implementing and monitoring the solution’s execution. This may involve controlling physical systems, adjusting parameters, or managing resources as required.
- Feedback Loop: AI can continuously monitor the problem and the effectiveness of the chosen solution. If the solution is not achieving the desired results or if new data indicates a change in circumstances, AI can adapt and refine the solution as needed.
- Learning and Adaptation: AI systems can learn from past problem-solving experiences and adapt their strategies for future problem-solving. This adaptive learning can improve the effectiveness of solutions over time.
- Human Interaction: In many cases, AI systems work in conjunction with human experts, who provide domain knowledge and guide the problem-solving process. Human-AI collaboration can enhance the quality of the solutions generated.
what is intelligence composed of Perception =
- Acquiring Data: Sensors are responsible for acquiring data from the environment. These sensors can be of various types, such as cameras for visual data, microphones for audio data, or environmental sensors for climate or physical data. AI systems interface with these sensors to gather raw data.
- Interpreting Data: Once the data is collected, AI algorithms are used to interpret it. The interpretation may involve several tasks:
- Feature Extraction: AI extracts relevant features from the raw data. For instance, in image processing, features could be edges, colors, or shapes.
- Object Recognition: AI identifies and classifies objects within the data. For example, in computer vision, AI can recognize and label objects in images.
- Speech Recognition: In the case of audio data, AI can transcribe spoken words or recognize voice commands.
- Natural Language Processing: For text data, AI can interpret and understand the meaning of written or spoken language.
- Selecting Relevant Information: Not all the acquired data is equally important. AI systems use various criteria to select the most relevant information for further processing or decision-making. This selection may be based on context, user preferences, or specific application requirements.
- Attention Mechanisms: AI can implement attention mechanisms to focus on specific regions or aspects of the data that are more relevant to the task at hand.
- Filtering and Preprocessing: AI may apply filters or preprocessing steps to remove noise or irrelevant information, enhancing the quality of the selected data.
- Feedback Loop: AI often operates in a feedback loop, continuously acquiring, interpreting, and selecting data. As new data becomes available, AI systems update their understanding and selection criteria, adapting to changing conditions and requirements.
what is intelligence composed of Learning
- Acquiring New Data: AI agents continuously gather new data from various sources. This data can come from sensors, databases, the internet, or user interactions. Learning often begins with data acquisition, as it provides the raw material for the AI agent to work with.
- Interpreting Data: Once the data is acquired, the AI agent interprets it to extract meaningful information. Interpretation may involve:
- Feature Extraction: Identifying relevant features or patterns in the data.
- Pattern Recognition: Detecting regularities or trends within the data.
- Categorization: Labeling or categorizing data into different classes or categories.
- Gathering Knowledge: The AI agent accumulates knowledge and experience over time through data acquisition and interpretation. This knowledge can be stored in databases, memory structures, or neural networks, depending on the learning approach.
- Selecting Relevant Information: AI agents, like humans, need to filter and select the most relevant data for further analysis and learning. They use various criteria to make these selections, such as the importance of the information for a specific task or its potential to improve performance.
- Attention Mechanisms: AI agents can implement attention mechanisms to focus on specific data points or features that are more relevant to the learning task.
- Relevance Scores: Assigning scores to data items based on their relevance to the learning objectives.
- Analysis and Learning: After selecting relevant information, AI agents analyze this data to learn and improve their performance. Learning can take different forms, such as:
- Supervised Learning: Learning from labeled data with known outcomes.
- Unsupervised Learning: Discovering patterns and relationships in data without labeled guidance.
- Reinforcement Learning: Learning through trial and error, where the agent receives feedback and adjusts its actions accordingly.
- Adaptive Behavior: The AI agent adapts its behavior and decision-making based on the knowledge and insights gained from the learning process. This adaptation can lead to improved performance in tasks, problem-solving, or decision-making.
- Feedback Loop: Learning is an ongoing process. AI agents continuously acquire, interpret, gather, select, and analyze data, adapting their knowledge and behavior over time. Feedback loops are essential to ensure that the agent remains up-to-date and can handle changing conditions.
what is intelligence composed of Linguistic Intelligence =
- Comprehending Verbal and Written Language:
- Speech Recognition: AI employs speech recognition technology to understand spoken language. This involves converting audio input into text, making it possible for AI to “comprehend” what is being said.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): For written language, AI uses NLP to comprehend and interpret text data. NLP techniques allow AI to understand the structure, meaning, and context of written language.
- Language Models: AI systems, particularly those based on deep learning, utilize language models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) to process and understand language. These models are trained on vast amounts of text data, enabling them to comprehend and generate human-like text.
- Language Translation: AI systems can translate text and spoken language from one language to another. They use machine translation techniques to facilitate cross-lingual communication.
- Text Analysis and Sentiment Analysis: AI is used to analyze large volumes of text data for various purposes, such as sentiment analysis, content categorization, and summarization. It can determine the emotional tone of text and make inferences about the writer’s feelings.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants use NLP to understand user queries and provide relevant responses. They can engage in text-based or voice-based conversations.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) and Speech Synthesis: AI can convert written text into spoken language using Text-to-Speech technology. This is particularly useful for voice assistants and accessibility applications.
- Language Generation: AI can generate human-like text, both verbally and in writing. This is used for tasks such as content creation, generating reports, or even creative writing.
- Language Translation and Localization: AI systems are used to translate written and spoken content to different languages, helping bridge language barriers in global communication.
- Grammar and Style Checking: AI tools assist in grammar and style checking for written content, ensuring that it is well-structured and error-free.
- Summarization: AI can summarize long articles or doc
Smart speaker with Alexa (Blue) buy now Virtual assistants: smart ai
what is intelligence composed of
36 ai features – what is artificial intelligence features
Ai history in legal advice -ai history filter -Foundational Concepts of AI
what is AI // क्या है ai //type of ai
Reinforcement learning- (RL)-What is RL in reinforcement?-introduction