Women’s Reservation Bill
Date 19 -24 sep
WHAT IS WOMAN ,S RESERVATION HISTRY IN INDIA
Women’s Reservation Bill
= NOTE = Remember that this is a political reservation bill, that is, there is talk of giving reservation in political power and not in jobs, officers, work.
Women’s Reservation Bill
1987 Rajiv Gandhi was the Prime Minister, at that time he recommended women for reform and there were 14 members in the formation of the Union Minister. Their work was mainly to protect women and bring them forward in the country because women were far behind in the country and people were facing atrocities on women. It was said that by protecting women, their seats should be fully booked, it was left at different times in different areas and it seems to be giving and going on even today, like if you are given so many seats for women in this area.
Reservation in cities and villages by one-third was provided by Rajiv Gandhi for women introduced for constitutional amendment
The Bill was passed by the Lok Sabha but it was not passed in the Rajya Sabha in September 1989
In 1992, Vipin Narasimha Rao made the 73rd and 74th constitutional amendments to the government.
1996 After the Constitution was amended to allow reservation for OBCs, there was a controversy in Parliament that reservation should be provided for women belonging to other backward classes (OBCs) once again.
In 1993, the Constitution was amended for inclusive women’s reservation, in which the main reservation was provided to one-third of the women in the gram panchayat, the village council leader or sarpanch
September 19 , 2023 There has been a 5-day recommendation or meeting in Parliament by Prime Minister Narendra Modi recommending providing 1-third reservation to women in Rajya Sabha or Lok Sabha and is likely to pass as BJP has maximum vote bank
TODY NEW 20-09-2023 IN INDIA
Women’s Reservation Bill
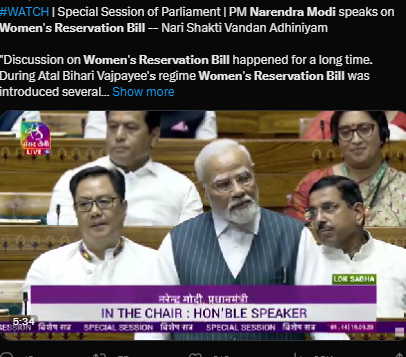
Cabinet clears 33% women reservation bill
The recent approval of the bill follows demands from various political parties and leaders for its passage during the special session of Parliament.
The Women’s Reservation Bill is seen as a significant step toward increasing gender representation in Indian politics.
The bill aims to address gender inequality in legislative bodies and promote the participation of women in decision-making roles in the country.
The Union Cabinet of India has cleared the Women’s Reservation Bill, which seeks to reserve 33% of seats for women in the Lok Sabha and state legislative assemblies.
For the first time, seat reservation for women in Rajya Sabha and Lok Sabha
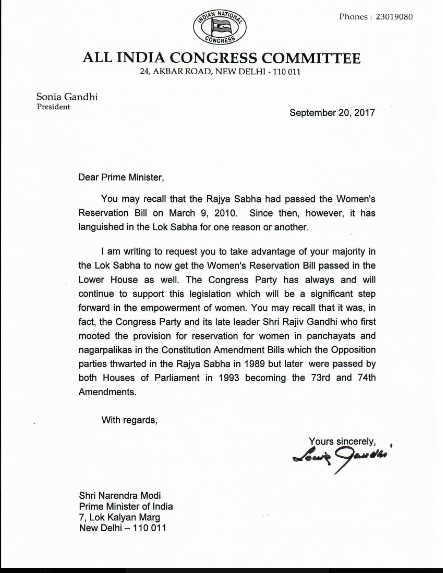
The bill was first introduced in the Rajya Sabha in 2008, passed in the upper house in 2010, but lapsed with the 15th Lok Sabha.
Women’s Reservation Bill
The Women’s Reservation Bill, also known as the Women’s Reservation Bill 2008, is a proposed law in India that provides for one-third of all seats in the Lok Sabha (the lower house of India’s Parliament) and state legislative assemblies to be reserved for women. The bill was first introduced in the Indian Parliament in 1996 and has been a subject of debate and discussion ever since.
-
The main objectives of the Women’s Reservation Bill are:
-
Women’s Reservation Bill
- Empowerment of Women: The bill aims to increase the political representation of women in India, as historically the representation of women in Indian politics has been low.
- Gender equality: It is seen as a step towards achieving gender equality and addressing the gender gap in politics.
- Political participation: By reserving seats for women, the Bill aims to encourage more women at all levels of government to participate in politics.
- Policy implications: Advocates argue that increased representation of women in politics can lead to policies and laws that better address issues affecting women, such as women’s rights, health care, education, and social welfare.
However, the Women’s Reservation Bill has faced huge opposition
Some of the reasons for the protest include concerns about the possible symbolism of reserving seats for women, questions about the selection process for women candidates and resistance from some political parties.
Despite the challenges and debates, this bill represents an ongoing effort to promote gender equality in politics in India and address the historic under-representation of women in the country’s political decision-making process.
FAQ
What is the meaning of women’s reservation?
Women’s reservation= refers to the practice of reserving a certain number of seats or positions in political, educational, or professional institutions specifically for women. This is done to ensure that women have equal opportunities and representation in these areas where they have historically been underrepresented.
Where are women’s seats reserved in India?
India, women’s seats are reserved in the Lok Sabha (the lower house of Parliament) and state legislative assemblies through the Women’s Reservation Bill, which proposes to reserve one-third of the total seats in these institutions for women.
What is the women’s reservation Act in India?
there is no specific “Women’s Reservation Act” in India. However, there is a proposed legislation called the “Women’s Reservation Bill” that seeks to reserve one-third of the seats in the Lok Sabha (the lower house of India’s Parliament) and state legislative assemblies for women. This bill has been under discussion and debate in the Indian Parliament for many years but had not been passed into law as of that time.
What is the women’s reservation under Article?
The provision for women’s reservation in India is primarily under Article 243D of the Indian Constitution. This article pertains to the reservation of seats for women in Panchayats (local self-government bodies at the village, intermediate, and district levels). It empowers states to reserve seats for women in these local governing bodies, ensuring their participation in grassroots-level governance. Additionally, Article 243T allows states to provide for similar reservations in Municipalities. These provisions are aimed at promoting gender equality and women’s participation in local governance.
more realeted blog read
mygov quiz chandrayaan 3-mygov quiz
Aditya-L1 mission quiz-50 quiz for Aditya mistion
g20-india middle east europe economic corridor map-G20 QUIZ
what is AI // क्या है ai //type of ai
Reinforcement learning- (RL)-What is RL in reinforcement?-introduction