-
Goal Based Agents

goal based agents in ai
Types of agents in AI
-
Simple Reflex Agents
-
Model Based Reflex Agents
-
Goal Based Agents
-
Utility Based Agent
-
Learning Agents
What is agent
It is the AI agents that help them and gives you results.
AI agent performs all type of tasks in an engine, just like there are all types of task in an engine, how they will speed up or when they will get a break, all these tasks are determineds.
What Are Goal-Based Agents?
goal based agents in ai are intelligent entities programmed to achieve specific objectives. These goals serve as their guiding principles, directing their actions and decisions. They perceive their environment, make choices based on the current context, and take actions to move closer to goal fulfillment.
-
Goal Based Agents work
goal based agents in ai are a fundamental concept in the field of artificial intelligence and agent-based systems. These agents are designed to perform tasks or achieve objectives in a way that simulates human decision-making and problem-solving.
- main focus → Completion of Goal
- Agents take decision based on how far it is currently from the Goal agent
- Every action is taken to minimize distance to Goal agent.
- More flexible Agent (know the goal)
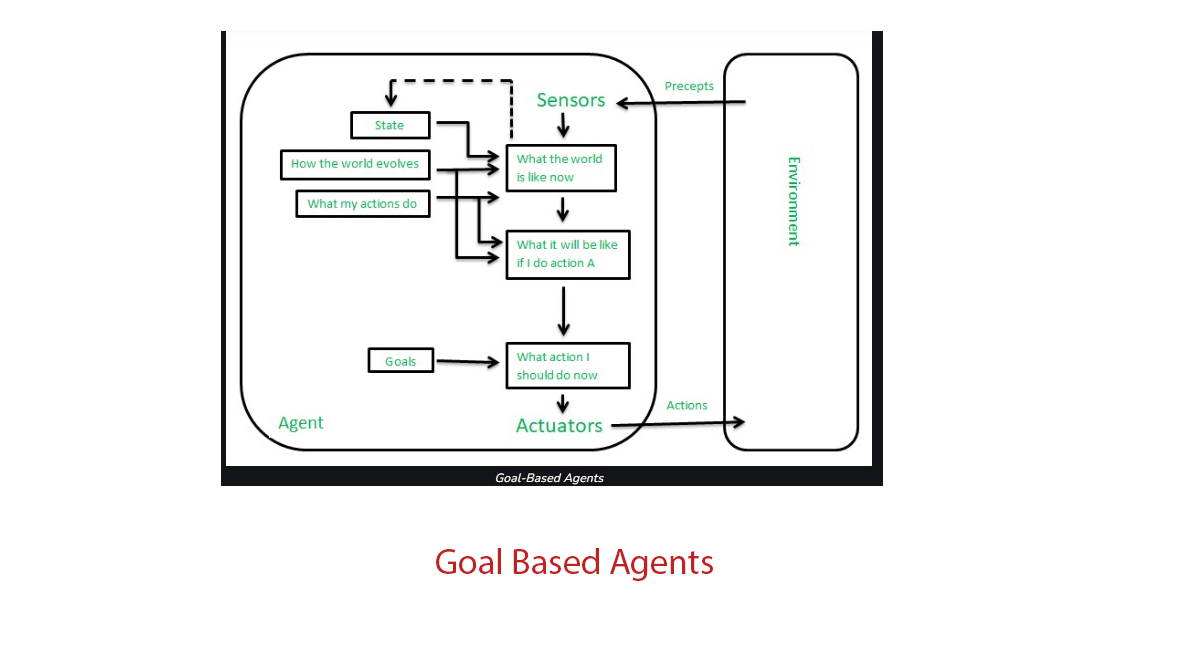
work
- Goal Definition: The first step in creating a goal based agents in ai is to define its objectives or goals. These goals represent what the agent aims to achieve. Goals can be specific tasks, such as finding the shortest path in a maze, playing a game, or managing a supply chain.
- Perception: goal based agents in ai typically have the ability to perceive their environment. This may involve using sensors, cameras, or other data sources to gather information about the current state of the world. In more complex scenarios, this can involve processing and interpreting sensory data.
- Reasoning and Decision-Making: Once the agent has perceived its environment, it engages in reasoning and decision-making processes to determine its actions. It evaluates the current state and compares it to its goals. Based on this evaluation, it selects actions that will bring it closer to achieving its goals. This decision-making process can be rule-based, algorithmic, or even based on machine learning techniques.
- Action Execution: After deciding on an action, the agent executes it in the environment. This can involve physical actions in the real world (e.g., a robot moving) or virtual actions in a computer program (e.g., selecting a chess move).
- Feedback and Adaptation: As the agent interacts with the environment and takes actions, it receives feedback. This feedback can be in the form of success or failure in achieving its goals, as well as information about the current state of the environment. The agent uses this feedback to adapt its decision-making and action-selection processes. It may adjust its strategies, change its goals, or learn from its experiences to improve its performance over time.
-
Goal Based Agents Introduction
goal based agents in ai are a fundamental concept in the field of artificial intelligence and autonomous systems. These intelligent agents are designed to emulate human-like decision-making and problem-solving, with a specific focus on achieving defined objectives or goals. Whether it’s a robot navigating through a cluttered environment, a computer program playing a game, or a virtual assistant completing tasks, goal based agents in ai play a crucial role in various applications. This introduction provides an overview of what goal-based agents are and how they function.
Features Goal Based Agents
- Goal Specification: goal based agents in ai have predefined objectives or goals that they aim to achieve. These goals serve as the basis for their decision-making processes. The specificity and clarity of these goals are crucial for the agent’s performance.
- Perception and Sensing: These agents are equipped with sensors or perception mechanisms to gather information about their environment. This may involve using cameras, microphones, sensors, or other data sources to assess the current state of the world.
- Reasoning and Decision-Making: goal based agents in ai engage in reasoning and decision-making processes to determine the most appropriate actions to achieve their goals. They evaluate the current state, compare it to their goals, and select actions accordingly. The decision-making can be rule-based, algorithmic, or based on machine learning techniques.
- Action Execution: Once a decision is made, goal based agents in ai execute actions in the environment. These actions can be physical, such as moving a robot or turning on a light, or virtual, such as making decisions in a computer program.
- Feedback and Learning: goal based agents in ai continuously receive feedback from the environment and the results of their actions. This feedback may include success or failure in achieving goals, as well as information about the current state of the environment. Agents use this feedback to adapt their strategies and improve their decision-making processes.
- Iteration: The process of perception, reasoning, decision-making, action execution, and adaptation is often iterative. Goal-based agents repeatedly cycle through these steps until their goals are met. This iterative nature allows them to learn and refine their strategies over time.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: While goal based agents in ai are driven by specific goals, they often have some degree of flexibility and adaptability. They can adjust their strategies and goals when needed, especially in response to changing environmental conditions.
- Multi-Objective Optimization: In some cases, goal based agents in ai may have to balance multiple objectives or goals simultaneously. They need to make trade-offs and prioritize actions to achieve a combination of goals efficiently.
- Resource Management: goal based agents in ai may need to manage resources effectively, such as time, energy, or budget, to achieve their goals. They make decisions that optimize the use of available resources.
- Real-World Applications: These agents find applications in various domains, including robotics, gaming, virtual assistants, navigation, and business optimization, among others. The specific features and capabilities of goal-based agents vary based on the application.
- Human Interaction: In some scenarios, goal based agents in ai interact with humans. This requires natural language processing and communication skills to understand user requests and provide appropriate responses.
- Ethical Considerations: Goal-based agents need to align their actions with ethical and social considerations, especially when their goals involve interacting with humans or making decisions that impact society.
-
Limitations Goal Based Agents
- Rigidity: goal based agents in ai are designed to achieve specific objectives. This can make them inflexible in situations where the goals need to change or adapt rapidly. If the goals are not well-defined or the environment is dynamic, the agent may struggle to adjust.
- Limited Problem Solving: goal based agents in ai excel at achieving predefined goals, but they may struggle with novel or unforeseen situations. They are typically not good at creative problem-solving or adapting to entirely new tasks.
- Sensitivity to Goal Specification: The effectiveness of a goal based agents in ai depends on how well the goals are defined. If goals are unclear or too narrowly defined, the agent may not perform optimally. Setting the right goals can be a challenging task.
- Inefficient Exploration: In complex and unknown environments, goal based agents in ai may need to explore different strategies and paths to achieve their goals. This exploration can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially if the agent doesn’t have prior knowledge about the environment.
- Overlooking Secondary Objectives: goal based agents in ai can become overly focused on their primary goals, potentially ignoring secondary objectives or unintended consequences. This can be problematic in situations where a broader perspective is required.
- Lack of Generalization: goal based agents in ai often learn specific strategies for achieving particular goals. They may struggle to generalize their knowledge and apply it to different but related tasks.
- Communication Challenges: In human-robot interaction or human-agent interaction scenarios, goal based agents in ai may not always understand or respond to natural language inputs effectively. They may require specific and structured commands.
- Complexity and Computation: For highly complex tasks, goal based agents in ai may require extensive computational resources, which can be expensive and slow. Real-time decision-making in complex environments can be challenging.
- Data Dependency: Many goal based agents in ai rely on data and feedback to make decisions and improve over time. If there is a lack of quality data or feedback, their performance may suffer.
- Ethical and Social Concerns: In some applications, goal based agents in ai can raise ethical and social concerns, especially when their goals are not aligned with human values or when they interact with humans in sensitive contexts.
- Resource Limitations: Physical goal based agents in ai like robots may be constrained by factors such as battery life, hardware limitations, and mobility, which can limit their effectiveness in certain environments.
-
Goal Based Agents examples
examples of goal based agents
- Autonomous Robots: Robots used in manufacturing, logistics, and even in households often employ goal-based agents. For instance, a warehouse robot may have the goal of efficiently moving goods from one location to another, while a vacuum-cleaning robot’s goal is to clean a room.
- Game-Playing AI: AI agents that play games, such as chess, Go, or video games, are goal-based agents. Their goal is to win the game by making optimal moves or decisions. Examples include Deep Blue for chess and AlphaGo for Go.
- Virtual Assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri, Google Assistant, and Alexa use goal-based agents to understand and fulfill user requests. The agent’s goal is to provide relevant information or perform tasks based on user input.
- Navigation Systems: GPS and mapping applications use goal-based agents to help users navigate from one location to another. The goal is to find the most efficient route based on user preferences and real-time traffic data.
- Chatbots: Goal-based chatbots are used in customer service and information retrieval. Their goal is to provide accurate responses and assist users with their queries, typically in a conversational manner.
- Recommendation Systems: E-commerce and content platforms like Amazon and Netflix use goal-based agents to recommend products or content to users. The agent’s goal is to increase user engagement or sales by suggesting relevant items.
- Medical Diagnosis Systems: AI systems designed to assist in medical diagnosis use goal-based agents. Their goal is to analyze patient data and symptoms to provide accurate diagnoses or treatment recommendations.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars and drones use goal-based agents to navigate and make driving or flying decisions. The goal is to reach a destination safely while avoiding obstacles and obeying traffic rules.
- Supply Chain Management: In logistics and supply chain management, goal-based agents help optimize inventory, routing, and distribution. Their goal is to reduce costs and improve the efficiency of the supply chain.
- Financial Trading: Algorithmic trading systems use goal-based agents to make decisions about buying or selling financial instruments. The goal is to maximize profits or minimize losses.
- Home Automation: Smart home systems that control lighting, heating, and security often use goal-based agents. The agent’s goal is to create a comfortable and secure living environment based on user preferences and sensor data.
- Energy Management: Goal-based agents are employed in energy management systems to optimize energy consumption in buildings and industrial facilities. The goal is to reduce energy costs while maintaining comfort and productivity.
Challenges and Future Developments
The future of goal-based agents holds exciting possibilities, from improved adaptability to enhanced problem-solving capabilities.
Real-World Examples
Let’s explore real-world examples of goal-based agents in action, showcasing their diverse applications.
The Role of Goal-Based Agents in Robotics
In robotics, goal-based agents play a pivotal role. They navigate complex environments, execute tasks, and adapt to unforeseen challenges.
Virtual Assistants and Chatbots
Virtual assistants and chatbots utilize goal-based agents to enhance user interactions and provide valuable services.
Goal-Based Agents in Gaming
From traditional board games to complex video games, goal-based agents exhibit exceptional gaming skills.
Goal-Based Agents in Business Optimization
In business and logistics, these agents optimize supply chain management, scheduling, and process efficiency.
Ethical and Social Implications
Exploring the ethical considerations when goal-based agents interact with humans and society at large.
Conclusion
Goal-based agents are the driving force behind many of the technological advances we see today. Their ability to emulate human-like decision-making, adapt to challenges, and achieve specific objectives make them indispensable in the world of artificial intelligence.
FAQs
- What is the primary function of goal-based agents? Goal-based agents are designed to achieve specific objectives by perceiving their environment, making decisions, and taking actions to fulfill those goals.
- In which industries are goal-based agents commonly used? Goal-based agents find applications in robotics, gaming, virtual assistants, business optimization, and more.
- Can goal-based agents adapt to changing goals and environments? Yes, goal-based agents can adapt to changing goals and dynamic environments, but their adaptability depends on how they are designed.
- What are some limitations of goal-based agents? Limitations include rigidity, limited problem-solving, and sensitivity to goal specification.
- What does the future hold for goal-based agents? The future promises enhanced adaptability and problem-solving capabilities, opening up new possibilities for their use.
Model based reflex agents examples
Smart speaker with Alexa (Blue) buy now Virtual assistants: smart ai
Model based reflex agents examples
What is simple reflex agents in ai
Model based reflex agents examples
what is an intelligent agent in ai
what is artificial intelligence composed of – ai
43 goals ai – future goals of ai – ankul belhi
36 ai features – what is artificial intelligence features
Ai history in legal advice -ai history filter -Foundational Concepts of AI
Model based reflex agents examples
what is AI // क्या है ai //type of ai
Reinforcement learning- (RL)-What is RL in reinforcement?-introduction
first Python programming-introduction Python programming
Model based reflex agents examples thank