Learning Agents

learning agent in ai
learning agent in ai example
Types of agents in AI
-
Simple Reflex Agent
-
Model Based Reflex Agents
-
Goal Based Agents
-
Utility Based Agent
-
Learning Agents
What is agents
It is the AI agents that help them and give you result.
AI agent perform all type of tasks in an engine, just like there are all type of tasks in an engine, how they will speed up or when they will get a break, all these tasks are determined.
Learning Agents
learning agent in ai from its Past experiences
Start to act with basic Knowledge & then able to act by adapting learning.
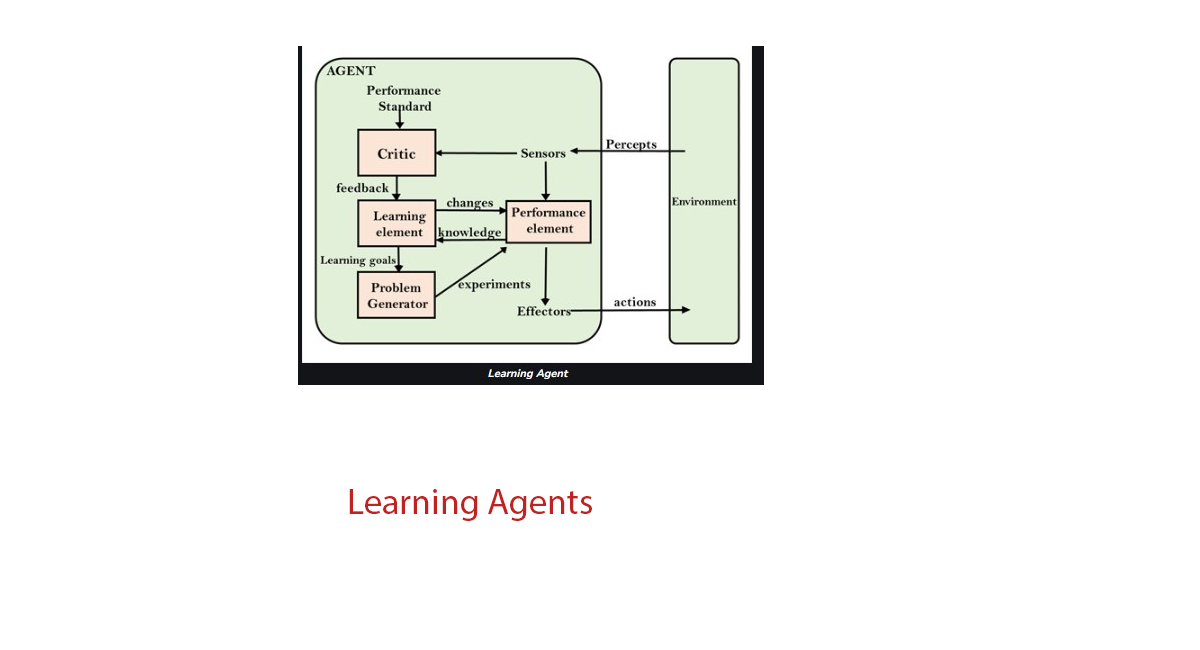
Components:–
- Learning element = improve system by learning from environment
- Citric = Check agent working & gives feedback.
- Problem Generator = suggest the taken do take & gain information
- Performance element → Select the action to Perform
Note = Alien agent is the most active on AI website
Using this, we are training AI. This agent is the biggest part of AI.
This agent trains himself and passes on his ideas to all the incoming workers and then further studies.
This agent can be broadly described as Machine learning, Unsupervised learning, Supervised learning, reinforcement learning, Deep learning, computational learning theory, Artificial neural network, Regression analysis, Computational complexity, sample complexity, Mathematical optimization or mathematical programming, classification, regression.
,Transfer learning,
Training is given through and the cost of providing their training is very high, but many websites have been created which work like virtual robots.
Example = chat gpt , google bard , text to image convert ,
What is Learning Agents
In the age of information, the ability to learn and adapt is a defining feature of intelligent systems. Learning agents, inspired by human learning processes, are at the forefront of AI research, enabling machines to acquire knowledge, make data-driven decisions, and continually improve their performance.
Indroduction Learning Agents
learning agent in ai are the backbone of artificial intelligence and machine learning, and they represent intelligent entities that can acquire knowledge, adapt to changing environments, and make informed decisions. In a world increasingly driven by data and automation, learning agents play a pivotal role in enhancing the capabilities of intelligent systems. They enable machines to continuously improve their performance by learning from experiences and interactions with the environment. This short introduction provides a glimpse into the significance of learning agents and their role in shaping the future of AI.
Types of Learning Agents
There are three main types of learning agents:
- Reactive Agents: These agents make decisions based on the current state of the environment, without considering past experiences. They react to the immediate situation.
- Memory-based Agents: Memory-based agents store and retrieve past experiences to make decisions. They learn by referencing historical data.
- Model-based Agents: Model-based agents create internal models of their environment and use them to simulate and plan future actions. They learn by refining their models.
The Learning Process
3.1 Data Collection
learning agent in ai collect data from their environment through sensors, cameras, or other data sources. This data provides the foundation for their learning process.
3.2 Learning Algorithms
learning agent in ai employ various learning algorithms to extract knowledge from the data they collect. These algorithms can be categorized into supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, depending on the learning objectives.
3.3 Adaptation and Improvement
Through continuous interactions with the environment and iterative learning cycles, learning agents adapt and improve their decision-making. They refine their knowledge and make better-informed choices over time.
Applications of Learning Agents
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use learning agents to navigate and make real-time decisions based on sensor data.
- Recommendation Systems: Platforms like Netflix and Amazon utilize learning agents to suggest content or products to users based on their preferences and behavior.
- Healthcare: learning agent in ai assist in diagnosing diseases, optimizing treatment plans, and predicting patient outcomes.
- Natural Language Processing: Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa employ learning agents to understand and respond to user queries.
- Finance: learning agent in ai are used in algorithmic trading, risk assessment, and fraud detection in the financial sector.
Learning Agents Features
- Learning Capability: learning agent in ai have the inherent ability to acquire knowledge and improve their performance over time. They do this by processing data and experiences, refining their models, and updating their decision-making processes.
- Adaptation: These agents excel in adapting to changing environments and circumstances. They can adjust their behavior and decision-making strategies based on new data and evolving conditions.
- Data Collection: learning agent in ai interact with their environment and collect data through sensors, cameras, or other data sources. This data serves as the foundation for their learning and decision-making processes.
- Learning Algorithms: They employ a variety of learning algorithms to extract knowledge from the data they collect. These algorithms include supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, depending on the learning objectives.
- Continuous Improvement: learning agent in ai engage in an iterative process of refinement. They continuously improve their knowledge, models, and decision-making capabilities through repeated learning cycles.
- Autonomy: These agents can make decisions independently, reducing the need for human intervention in various tasks and applications. Their autonomy is particularly valuable in settings like autonomous vehicles and smart systems.
- Pattern Recognition: learning agent in ai are proficient in recognizing patterns and trends within the data they process. This ability allows them to make predictions, classify information, and detect anomalies.
- Customization: They can be customized to suit specific learning objectives and application domains. Learning agents are adaptable to various industries, from healthcare to finance and education.
- Real-Time Decision-Making: In applications like autonomous vehicles and robotics, learning agent in ai make real-time decisions based on incoming data. Their ability to process and respond to data rapidly is critical for these applications.
- Diverse Applications: learning agent in ai are employed across diverse industries, including healthcare for disease diagnosis, finance for algorithmic trading, and recommendation systems for personalized content suggestions.
- Ethical Considerations: Ensuring ethical behavior and mitigating biases in learning agents is a growing concern. Researchers and developers are actively working to address these issues, making ethical decision-making a feature in itself.
- Future Potential: learning agent in ai hold immense potential for the future of AI and machine learning. Advancements in algorithms and technologies continue to expand their capabilities and applications in numerous fields.
Learning Agents limitations
- Data Dependency: learning agent in ai heavily rely on data for training and decision-making. If the data is scarce, biased, or of poor quality, it can lead to inaccurate or biased decisions.
- Overfitting: learning agent in ai can become overly specialized in the training data, leading to poor generalization to new, unseen data. Overfit models can perform well on training data but poorly on real-world tasks.
- Computational Resources: Many learning algorithms require significant computational resources, which can limit the deployment of learning agents in resource-constrained environments.
- Data Privacy and Security: In applications where sensitive or personal data is involved, the use of learning agents may raise privacy and security concerns. Safeguarding data and ensuring compliance with regulations is essential.
- Ethical Concerns: learning agent in ai can inadvertently inherit biases present in the training data, leading to biased decision-making. Ensuring ethical behavior and preventing discrimination is a challenging issue.
- Interpretablility: Some learning algorithms, like deep neural networks, can be highly complex and challenging to interpret. This lack of transparency can be problematic in applications where decisions need to be explained or validated.
- Concept Drift: learning agent in ai may struggle to adapt to rapidly changing environments or scenarios where the relationships between variables change over time. This concept drift can lead to performance degradation.
- Lack of Common Sense: learning agent in ai do not possess common sense reasoning like humans. They rely solely on patterns in data, which can limit their ability to make context-aware decisions.
- Resource Intensive Training: Training learning agent in ai can be resource-intensive and time-consuming. It may take significant computational power and data to create effective models.
- Limited Transferability: Models trained for one specific task or domain may not easily transfer to another. This lack of transferability necessitates retraining for each new task.
- Safety Concerns: In safety-critical applications like autonomous vehicles or healthcare, the consequences of errors made by learning agents can be severe. Ensuring safety is a paramount concern.
- Human Interaction Challenges: Interactions between learning agent in ai and humans can be challenging. Ensuring effective communication and understanding user needs is an ongoing area of research.
- Complexity: Complex learning models can be challenging to develop, deploy, and maintain. Their complexity may require specialized expertise and resources.
- Inherent Uncertainty: learning agent in ai must operate in uncertain environments and may not always make perfect decisions. Handling uncertainty and risk management is an ongoing challenge.
- Scalability: While learning agent in ai work well in many applications, they may face scalability challenges in very large and complex problem domains.
Learning Agents examples
learning agent in ai example
- Self-Driving Cars: Autonomous vehicles use learning agents to navigate roads, interpret sensor data, and make real-time decisions. They continuously learn from driving experiences to improve safety and efficiency.
- Recommendation Systems: Platforms like Netflix and Amazon employ learning agents to provide personalized content recommendations to users based on their viewing history, preferences, and behavior.
- Healthcare Diagnosis: Learning agents assist medical professionals by analyzing patient data, such as medical images and diagnostic records, to aid in disease diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Algorithmic Trading: In the financial sector, learning agents are used in algorithmic trading systems. They analyze market data, historical trends, and news feeds to make automated trading decisions.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa use learning agents to understand and respond to voice commands. These agents continually improve their understanding of natural language by learning from user interactions.
- Chatbots: Customer service chatbots employ learning agents to understand user queries and provide responses. They learn from customer interactions to improve the quality and relevance of their responses.
- Reinforcement Learning in Gaming: Learning agents are used in video games to control non-player characters (NPCs). These agents learn to adapt to player strategies, making game environments more dynamic and engaging.
- Fraud Detection: In the banking and e-commerce sectors, learning agents help detect fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction data and identifying suspicious patterns.
- Language Translation: Language translation services like Google Translate use learning agents to improve the accuracy of translations by learning from a vast dataset of multilingual content.
- Smart Home Systems: Learning agents are integrated into smart home devices and systems, enabling them to adapt to user preferences, optimize energy usage, and enhance security.
- Educational Technology: Learning agents are applied in e-learning platforms to provide personalized learning experiences. They analyze student performance data and adapt the curriculum to individual needs.
- Content Creation and Curation: Content platforms use learning agents to generate and curate articles, videos, and music playlists. These agents can understand user preferences and create or suggest content accordingly.
- Robotics: In robotics, learning agents help robots perform tasks like object recognition, navigation, and manipulation. They continuously learn from their interactions with the physical world.
- Agriculture: Learning agents are used in precision agriculture for crop monitoring and management. They analyze data from sensors and drones to optimize irrigation and fertilization.
- Energy Management: Learning agents optimize energy consumption in buildings and industrial facilities. They analyze data from sensors and devices to make real-time decisions for efficient energy usage.
The Future of Learning Agents
The future of learning agents holds promise in areas like more advanced machine learning algorithms, enhanced adaptation to dynamic environments, and broader applications in healthcare, education, and beyond. As AI technology continues to advance, learning agents will play a pivotal role in shaping the intelligent systems of tomorrow.
Conclusion
Learning agents represent a crucial advancement in the field of AI, enabling machines to learn, adapt, and make data-driven decisions. Their applications span various industries, and their potential for continuous improvement offers exciting possibilities for the future of intelligent systems.
FAQs
- How do learning agents acquire knowledge? Learning agents acquire knowledge by collecting data from their environment and using learning algorithms to extract meaningful information.
- What are the main types of learning agents? The main types of learning agents are reactive agents, memory-based agents, and model-based agents.
- In which industries are learning agents commonly used? Learning agents find applications in autonomous vehicles, healthcare, finance, recommendation systems, and natural language processing, among others.
- What are the challenges in implementing learning agents? Challenges include data quality, computational complexity, and ethical concerns regarding biased decision-making.
- What does the future hold for learning agents? The future of learning agents involves more advanced machine learning algorithms, improved adaptation to dynamic environments, and expanded applications in various sectors.
learning agent in ai
Smart speaker with Alexa (Blue) buy now Virtual assistants: smart ai
learning agent in ai
goal based agents in ai
utility-based agents in ai
Model based reflex agents examples
What is simple reflex agents in ai
36 ai features – what is artificial intelligence features
Ai history in legal advice -ai history filter -Foundational Concepts of AI
learning agent in ai
what is AI // क्या है ai //type of ai
Reinforcement learning- (RL)-What is RL in reinforcement?-introduction
first Python programming-introduction Python programming